Describe 4 Different Uses of Biotechnology Genetic Engineering
A genetically modified organism GMO is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniquesThe exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies with the most common being an organism altered in a way that does not occur naturally by mating andor natural recombination. This is a unique aspect because the HGP is the first large scientific endeavor to address social issues that may arise from the project 3.

Biotechnology Applications Of Biotechnology Britannica
Genetic engineering also called genetic modification is the direct manipulation of an organisms genome using biotechnology.

. Genetic engineering also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation is the direct manipulation of an organisms genes using biotechnologyIt is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organismsNew DNA is obtained by either isolating. Or by synthesizing the DNA and then inserting this construct into the host organism. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular-cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence.
Genome editing is a process where an organisms genetic code is changed. The DOE and NIH genome programs each set aside 3-5 of their annual. The more cell types a cell can differentiate into the greater its potency.
Scientists use enzymes to cut DNA creating a double-strand break DSB. The genetically modified microbes are also effectively used in biomining and. Cell potency is a cells ability to differentiate into other cell types.
ELSI was created so that potential problem areas could be identified and solutions created before genetic information is integrated into modern health care practices 4. Likewise genetic engineering strategies have been employed to tackle the environmental issues such as converting wastes into biofuels and bioethanol 47 cleaning the oil spills carbon and other toxic wastes and detecting arsenic and other contaminants in drinking water. NHEJ produces random mutations gene knockout while HDR uses additional DNA to create a desired sequence.
DSB repair occurs by non-homologous end joining NHEJ or homology-directed repair HDR. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell which like a continuum begins with totipotency to designate a cell with the most differentiation potential pluripotency multipotency oligopotency and finally unipotency.

Applications Of Genetic Engineering Advantages And Disadvantages Genetic Engineering Genetics Study Biology
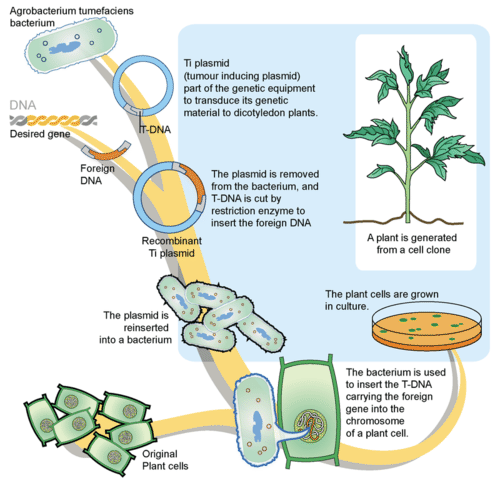
Applications Of Biotechnology In Agriculture Ck 12 Foundation

8 2 Biotechnology And Genetic Engineering Environmental Biology
No comments for "Describe 4 Different Uses of Biotechnology Genetic Engineering"
Post a Comment